Studying the Inductive Biases of RNNs with Synthetic Variations of Natural Languages
 Synthetic variations of Enlglish allow us to assess the influence of different linguistic propeties on the ability of neural models to acquire syntax.
Synthetic variations of Enlglish allow us to assess the influence of different linguistic propeties on the ability of neural models to acquire syntax.Abstract
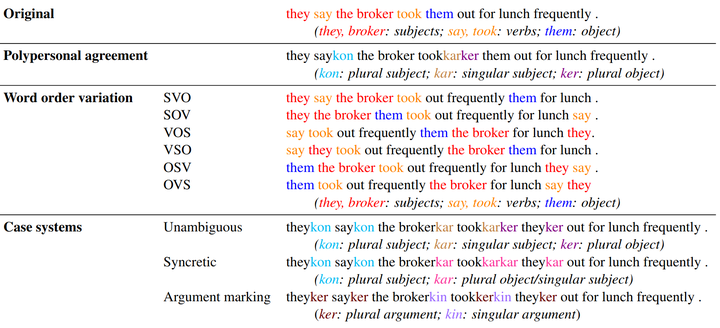
How do typological properties such as word order and morphological case marking affect the ability of neural sequence models to acquire the syntax of a language? Cross-linguistic comparisons of RNNs’ syntactic performance (e.g., on subject-verb agreement prediction) are complicated by the fact that any two languages differ in multiple typological properties, as well as by differences in training corpus. We propose a paradigm that addresses these issues: we create synthetic versions of English, which differ from English in one or more typological parameters, and generate corpora for those languages based on a parsed English corpus. We report a series of experiments in which RNNs were trained to predict agreement features for verbs in each of those synthetic languages. Among other findings, (1) performance was higher in subject-verb-object order (as in English) than in subject-object-verb order (as in Japanese), suggesting that RNNs have a recency bias; (2) predicting agreement with both subject and object (polypersonal agreement) improves over predicting each separately, suggesting that underlying syntactic knowledge transfers across the two tasks; and (3) overt morphological case makes agreement prediction significantly easier, regardless of word order.